Developer training - fundamentals
Creating financial markets technology today is fundamentally broken – too slow, expensive and high-risk. Genesis is revolutionising software delivery within the financial markets so that any coder can create reactive, performant and compliant applications in days.
The aim of this page is to give you a high-level understanding of the Genesis low-code development platform, taking you through what it is, why it is and what it does. This will include the following topics:
- why we created the Genesis Low-code platform
- what the Genesis platform is
- building blocks and components
- platform tooling
- architecture and technology
- application elements
- demo
Genesis low-code platform
What is a platform?
One definition of a platform is a complete software programming development environment and underlying subsystem (Forbes, 2015). This could be a combination of language, runtime, libraries, and supporting tooling. It's more than just a framework but might include one. In practice, it is anything that you can build upon.
The Genesis Low-code platform has specific software architecture, application design, deployment, monitoring and levels of abstraction available. These fundamentals have been purpose-built to help accelerate developers, and to offer as much flexibility for use-cases as possible.
What is a low-code platform?
"A low-code application platform is an application platform that supports rapid application development, one-step deployment, and execution and management using declarative, high-level programming abstractions, such as model-driven and metadata-based programming languages. They support the development of user interfaces, business logic and data services; improve productivity; and are typically delivered as cloud services."
Gartner, 2022
The Genesis Platform is targeted at developers. We help them to decrease time-to-market, increase application velocity and lower the cost of development.
What can I build with the Genesis Platform?
While being flexible enough to cover most application use-cases, it also provides some foundational components for high-performance, low-latency applications. Central to our architecture is an event-driven system that can scale to millions of events per day with easy fan-out to connected web clients.
Here are some examples:
Non-functional
- real-time data subscriptions
- low-latency feed ingestion
- high transaction volume
- secure APIs
- high availability and clustering.
- integration with LDAP or SAML (SSO)
Data
- aggregated data views
- ad-hoc req/response queries
- stream data from/to external relational databases
- full audit trail is automatically provided
Application
- event handlers for applying custom business logic
- permissioned access
- workflow and auditing requirements
- responsive, rich user workflows and UI
Functional
- process financial instruments
- event-driven processing triggered by user actions or rules
- calculation of positions, data consolidation in general
Building blocks
Back to the definition
A low-code application platform is an application platform that supports rapid application development, one-step deployment, and execution and management using declarative, high-level programming abstractions, such as model-driven and metadata-based programming languages. These features support the development of user interfaces, business logic and data services. They improve productivity, and the resulting products are typically delivered as cloud services.
Core platform components
The core platform components form a common base; they work with other platform elements to enable enterprise-ready features with very little build effort.
Here are some examples for you to consider:
| BUILDING BLOCKS / COMPONENTS | CAPABILITIES |
|---|---|
| Auth Manager, Perms Manager | Provides industrial-strength authentication and entitlements management. |
| Cluster | Enables high-availability and horizontal scaling. |
| Router, Connect, Services Repository | UI connectivity and load balancing to server services. |
| Database API, NOSQL, SQL | High-performance persistence supporting next-generation database technologies. |
Technical components
The technical components enable you to develop scalable apps quickly and efficiently, based on event-driven architecture and real-time data distribution.
Examples of technical components are:
| EXAMPLE BUILDING BLOCKS / COMPONENTS | CAPABILITIES |
|---|---|
| Transactional, Handler | Process high throughput and highly complex transactions. |
| Event Handler | Allows event-driven architecture and complex event processing. |
| Data Server | Real-time data distribution in highly performant, low latency and complex structures. |
| Consolidation Manager | Efficient data consolidation and analytics. |
Business integration
With our expertise, we can combine business with technical components to provide key functionality and connections for working in financial markets:
| EXAMPLE | CAPABILITIES |
|---|---|
| FIX | FIX messaging. |
| Bloomberg TOMS | Bloomberg TOMS for treasury trading. |
| Murex | Integration with legacy vendor Murex. |
| ION Trading | Integration with the Fidessa OMS. |
| Pershing | Comprehensive integration to Nexus. |
| SS&C Geneva | Trades, positions, balances & margin requirements. |
Custom components
Custom components configure purpose-specific microservice components that extend functionality while remaining scalable. This allows you to :
- create using your choice of languages, including Java, Groovy, or R
- enable seamless app functionality with database access, component management, and component orchestration
- deliver lasting benefits with resilience and scalability
Micro front-ends
Micro-front-end architecture is a design approach in which a front-end app is decomposed into individual, semi-independent micro applications working loosely together.
We've built out a number of re-usable micro-front-ends that can be used by Genesis-powered applications:
| MICRO FRONT-END | CAPABILITIES |
|---|---|
| Foundation Reporting | The Reporting micro front-end enables your users to create report specifications, run them, or save them for later use. |
| Foundation Header | The Header micro front-end is a semi-batteries-included component. It consists of a navigation bar and flyout menu, with routing and account-logout capabilities. |
| Foundation Entity Management | The Entity Management micro front-end is used to connect to a resource on the back end and manage it from the front end. |
| Foundation Login | This Login micro front-end includes a set of identity management functions, such as authentication (including via SSO) and password reset. |
| Foundation Testing | This testing provides shared unit and e2e testing functionality. |
| Foundation Forms | The forms is a library for efficient building complex forms and filters at scale. |
| Foundation Layout | This layout provides a very easy way to configure the layout of the page. |
| Foundation Comms | This Comms provides a collection of comms services and utilities. |
Platform tooling
Genesis tools enable developers to bring their visions to life, quickly.
In the table below we can see a number of Genesis tools, their uses and capabilities.
| USE | EXAMPLE TOOLS | CAPABILITIES |
|---|---|---|
| Create | Genesis SDK | Framework for building Genesis applications in Low Code with the Genesis Platform Language. |
| Migrate | Excel Integration | Transform Excel worksheets into Genesis applications and synchronize cells in real time. |
| Migrate | DB Integration | Transform relational databases into Genesis applications and synchronize data in real time. |
| Operate | GEM | Cloud-agnostic management and auditing of Genesis environments. |
| Operate | Console | Monitoring status, exploring log files and querying application data. |
| Operate | Intellij Plugin | Enables you to run the full stack of a Genesis application locally within IntelliJ, so you can check and test your development work as you progress. |
| Assistance | Genny | An AI bot to provide code examples and clarification about Genesis and all its components. |
| Assistance | Genesis copilot | An AI code assistant to provide suggestions of code while the developer is coding. |
| Assistance | Platform AI Service | We have designed a Platform AI service layer offering prebuilt AI powered business components. |
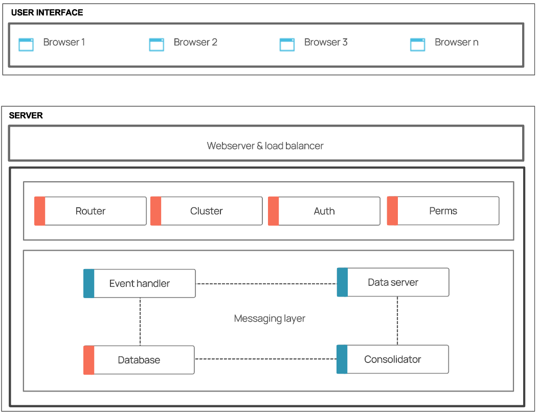
Platform architecture
The Genesis low-code platform has a real-time event-driven architecture built with microservices:
- Scale and fail independently.
- Develop with agility.
- Audit with ease.
Below we have a diagram demonstrating the components within the User Interface as well as the server.
Application elements
Elements of any application
When it comes to creating applications using the Genesis Platform, there are some elements will be in almost every application. So we recommend five main steps:
- Define your Data Model.
- Define your Business Logic.
- Integrate with other Systems.
- Create User Interfaces.
- Control Access.
These five steps are a roadmap for creating an application, and they are the basis of the tutorials in this course.
The elements of any application
GPAL
The elements of any Genesis Platform app are powered by a type-safe layered system which combines an easy-to-learn Kotlin-based Domain Specific Language (DSL) with transparent references between layers to ensure code changes are minimal when working with our technical components (e.g. Data Servers, Event Handlers, Request Servers, etc) and our data schema layer.
- The different layers of the architecture are: configuration | fields schema, tables schema | view schema | runtime.
- Each layer has its own Kotlin DSL plus specific code generation attached to it.
- Each layer also builds on top of the previous one, so changes in the bottom can be propagated to the next layers on top (i.e. changes in the fields schema could affect runtime DSL).
Why GPAL?
- To accelerate development with a concise and integrated way to declare configuration and even business logic.
- Any changes in a component are reflected automatically in the metadata exposed by our server endpoints, so any consumer of them (including our Web framework) can understand exactly what each endpoint expects as an input and provides as an output.
- This is incredibly useful when building a solution, as it allows us to self-inflate grids and forms automatically using our tools (i.e. Genesis Console) so we can discover, test and visualize a whole server environment without writing a single line of UI code.
GPAL
Let’s see how it works with some practical examples.
Configuration file
systemDefinition {
global {
item(name = "NULLABILITY_FOR_TRADE_FIELDS", value = "false")
}
}
Fields file
fields {
field(name = "COUNTERPARTY_ID", type = STRING)
field(name = "COUNTERPARTY_CODE", type = STRING, nullable = false)
field(name = "INSTRUMENT_ID", type = STRING)
field(name = "INSTRUMENT_CODE", type = STRING)
field(name = "ALTERNATE_TYPE", type = STRING, nullable = false)
field(name = "NAME", type = STRING)
field(name = "ENABLED", type = BOOLEAN)
field(name = "COUNTERPARTY_LEI", type = STRING)
field(name = "MARKET_ID", type = STRING)
field(name = "COUNTRY_CODE", type = STRING)
field(name = "CURRENCY_ID", type = STRING)
field(name = "ASSET_CLASS", type = STRING)
}
Data model and configuration
As seen in the code sample below, automatic auditing and the reuse of fields with intellisense are allowed for. As well as this, data model changes can be made without DBA.
table(name = "TRADE", id = 11000, audit = details(id = 11000, sequence = "TA", tsKey = true)) {
sequence(TRADE_ID, "TR")
INSTRUMENT_ID
COUNTERPARTY_ID
QUANTITY
SIDE
PRICE
TRADE_DATETIME
ENTERED_BY
TRADE_STATUS
primaryKey{
TRADE_ID
}
}
table(name = "INSTRUMENT", id = 11001, audit = details(id = 11001, sequence = "IA", tsKey = true)) {
sequence(INSTRUMENT_ID, "IN")
INSTRUMENT_NAME
primaryKey{
INSTRUMENT_ID
}
}
table(name = "COUNTERPARTY", id = 11002, audit = details(id = 11002, sequence = "CA", tsKey = true)) {
sequence(COUNTERPARTY_ID, "CP")
COUNTERPARTY_NAME
primaryKey{
COUNTERPARTY_ID
}
}
Data views
view ("TRADE_VIEW", TRADE) {
joins {
joining(COUNTERPARTY) {
on(TRADE.COUNTERPARTY_ID to COUNTERPARTY.COUNTERPARTY_ID)
}
joining(INSTRUMENT) {
on(TRADE.INSTRUMENT_ID to INSTRUMENT.INSTRUMENT_ID)
}
}
fields {
TRADE.allFields()
COUNTERPARTY.NAME withPrefix COUNTERPARTY
INSTRUMENT.NAME withPrefix INSTRUMENT
derivedField("CONSIDERATION", DOUBLE) {
withInput(TRADE.QUANTITY, TRADE.PRICE) { QUANTITY, PRICE ->
QUANTITY * PRICE
}
}
}
}
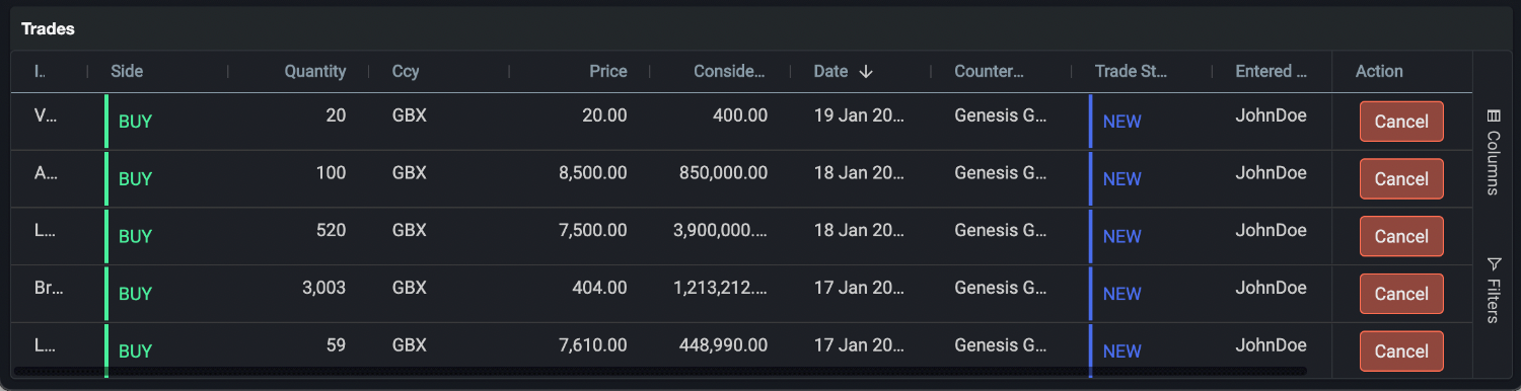
Distributing data
As can be seen in the code snippets below, the platform handles connection management and data streaming out of the box and binds actions to event handlers.
dataServer{
query("ALL_TRADES", TRADE_VIEW)
}
<zero-grid-pro rowHeight="45">
<grid-pro-genesis-datasource resourceName="ALL_TRADES" orderBy="TRADE_DATETIME" />
</zero-grid-pro>
Business logic
A typical Event Handler file can be seen below:
eventHandler{
eventHandler<Trade>(name = "TRADE_INSERT"){
onValidate { event->
val trade = event.details
verfiy{
entityDb hasEntry Counterparty.ById(trade.counterpartyId)
entityDb hasEntry Instrument.ById(trade.instrumentId)
}
ack()
}
onCommit { event ->
val trade = event.details
trade.enteredBy = event.userName
entityDb.insert(trade)
ack()
}
}
}
With GPAL all layers are well integrated and a single change is propagated to the others.
This makes it easy to learn and removes a lot of unnecessary code.
Automatic integration
Microservices and resources built as part of any Genesis application will have automatic and native API support.
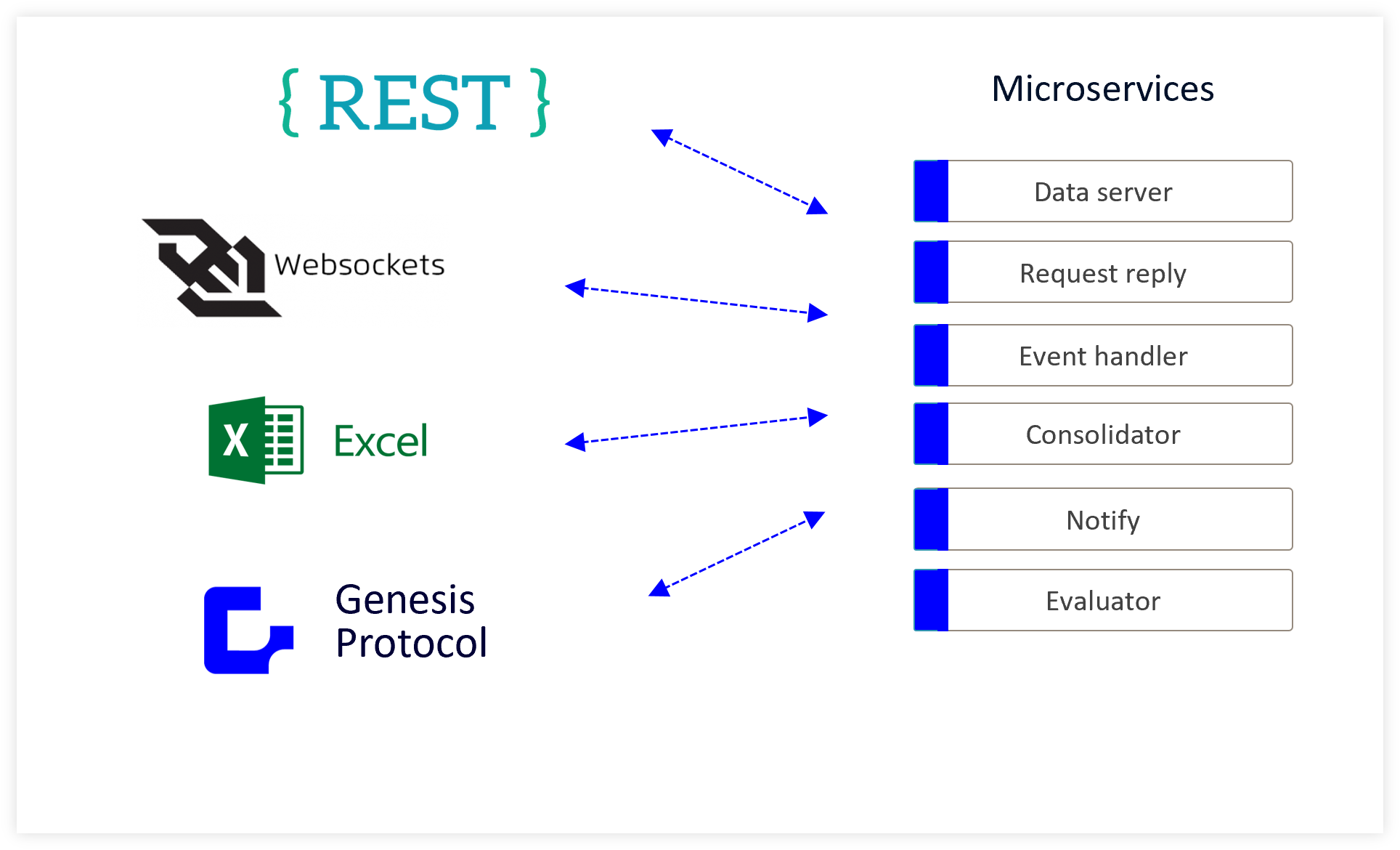
Integrations
Genesis supports a wide range of third-party integrations. Some of these are listed here:

Data model configuration
- built for the financial markets
- Genesis Web Components for performance and accessibility
- composed into micro front-ends
Genesis web components provide reusable building blocks and app functionality that works seamlessly with today’s popular web frameworks - and any that might become popular in the future.
Platform capabilities
- supercharging developers: enhancing productivity of professional developers with full-stack development expertise
- powerful framework, runtime & tools: full-featured framework and tools for building financial-markets applications
- proven enterprise-grade solutions: Range of standalone applications in production across use cases, from spreadsheet replacements to high-performance core applications
The Genesis Platform has been developed on the back of years of experience delivering software applications for some of the largest financial firms in the world. There was a clear need for a more targeted approach to support the requirements of financial markets software.
Custom logic and behaviour can be added where needed and being built on the JVM, it enables access to a mature ecosystem of libraries used in the industry.
The platform includes a modern, high-performance web-application solution, enabling developers to build branded UIs quickly using data models and the real-time features of the server.
Our web stack is built using modern web platform features, integrating easily with existing web stacks such as Angular and React.
As well as this, the Genesis Platform provides some foundational components for high-performance, low-latency applications. Central to our architecture is an event-driven system that can scale to millions of events per day with easy fan-out to connected web clients.
Next steps
Let's get you set up!