Entity Management
The entity-management micro front-end gives you a grid and a form that you can add to your pages and configure.
- The grid takes its data from a specified resource in the back end - a Data Server
queryor a Request ServerrequestReply. - You can then add Create and Edit events to the definition; each event automatically generates a form from the metadata of the back-end resource; it also adds buttons to the grid automatically so that the user can click to access the forms. You can also add a Delete event to the definition, which automatically displays a Delete button, which the user can click on to delete the relevant record.
The event buttons are accessed conditionally. For example, if the current user is only able to edit the entities, then you should only set the edit event on the entity-manager - you need to set the events so that they are conditional on user authorisations.
Set-up
- Add
@genesislcap/foundation-entity-managementas a dependency in your package.json file. Whenever you change the dependencies of your project, run the$ npm run bootstrapcommand again.
{
...
"dependencies": {
"@genesislcap/foundation-entity-management": "latest"
},
...
}
- Import and declare the class in the page of the class where you wish to use the Entity Manager.
// Import
import { EntityManagement, } from '@genesislcap/foundation-entity-management';
// Declare class
EntityManagement;
Now you are ready to implement entity-management in the relevant template html.
Implementing
Here is a simple example of entity-management, which can be inserted into a page.
<entity-management
resourceName="ALL_INSTRUMENTS"
title = "Instruments"
createEvent = "EVENT_INSTRUMENT_INSERT"
></entity-management>
`;
In this example, we have used three attributes when declaring the entity-management micro front-end:
resourceName="ALL_INSTRUMENTS"defines the source of the data for the grid: a Data Server query called ALL INSTRUMENTS.title = "Instruments"displays this text as the title of the grid.createEvent = "EVENT_TRADE_INSERT"generates a form with all the fields from the metadata of the event and adds a button at the top of the grid so that the user can access this form.
With this code in place, you can see the grid in your page if you run the application locally (as long as your back end has the correct resources).
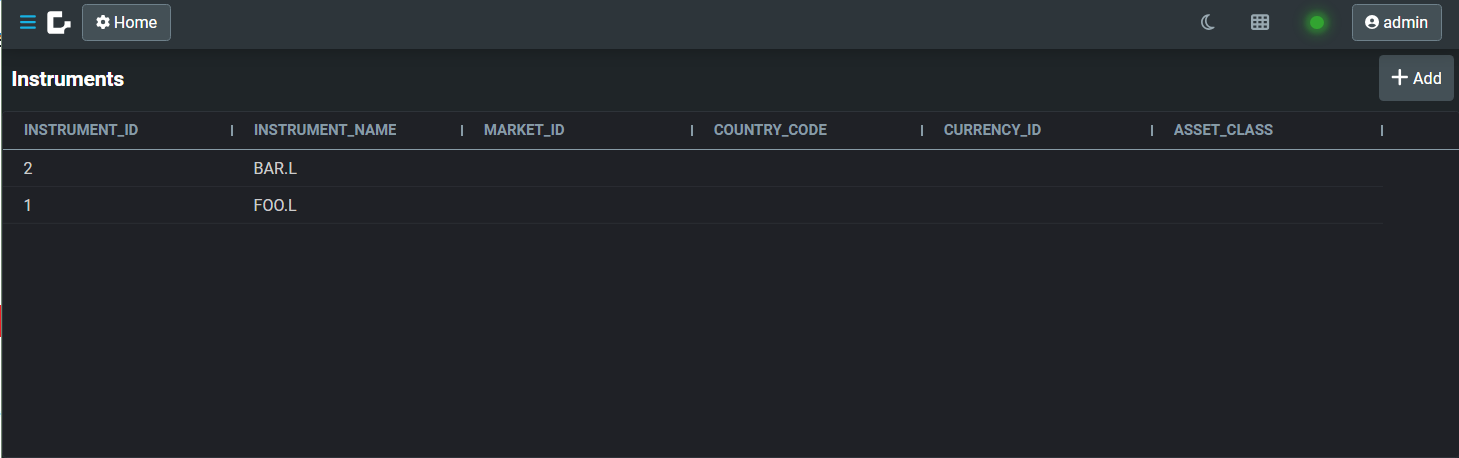
And you can click on the Add button to view the form.
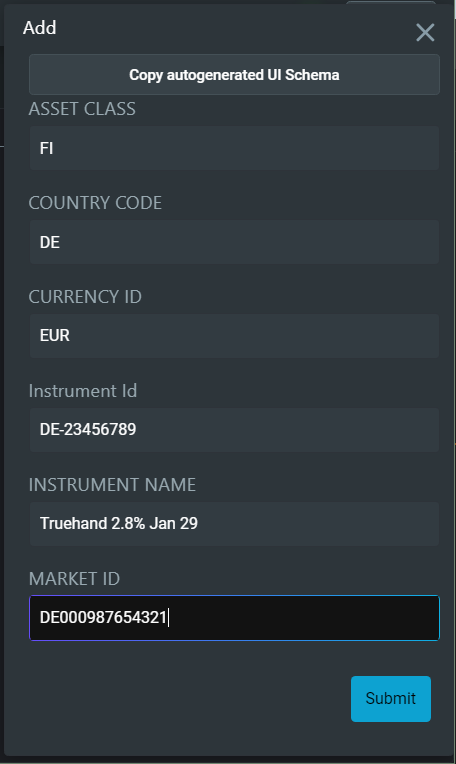
Common attributes
The most common attributes you can configure for entity-management are listed below. Note that it is not mandatory to specify an event, but if you don't specify a createEvent or an updateEvent, then you won't have a form created - which defeats the point of using this micro front-end. It would be simpler to use a grid-pro or data grid.
| Attribute | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
title | customises the title of the entity list so that the user can see what resource they are managing. | Yes |
resourceName | specifies the name of a resource on the server: a query in the Data Server, a ReqRep in the Request Server or an eventHandler in the Event Handler. | Yes |
createEvent | specifies an event on the back end for adding a record to the table; once specified, this displays an Add button above the grid. | No |
updateEvent | specifies an event on the back end for modifying a record in the table; once specified, this displays an Edit button to the right of every record in the grid. | No |
deleteEvent | specifies an event on the back end for deleting a record in the table; once specified, this displays a Delete button to the right of every record in the grid. | No |
datasourceConfig | configures the interaction with the back-end resource. | No |
defaultEntityValues | an object that contains default values to populate the form when the user is adding an entity. | No |
persist-column-state-key | the user can change columns (the width, for example); if you want the column states to be persisted when the user navigates away from the page, specify a unique string value. By default, changes are not persisted, and the grid returns to its default state every time the user navigates away from it. | No |
columns | enables you to supply an array of ColDef[] properties to customise the grid. | No |
createFormUiSchema | enables you to supply a schema to configure an insert form. | No |
updateFormUiSchema | enables you to supply a schema to configure an update form. | No |
crud-menu-position | specifies the position of the CRUD action buttons (Add, Edit, Delete) within the grid. Possible values are: column, top, bottom, none (no menu displayed) | No |
crud-menu-style | defines the visual style of the CRUD action buttons. Possible values are default (displays the buttons side by side), actions-vertical (displays a small button with three vertical dots; when the user clicks on this small button, the available CRUD options are displayed vertically), actions-horizontal (displays a small button with three vertical dots; when the user clicks on this small button, the available CRUD buttons are displayed horizontally) | No |
crud-action-menu-name | defines the label used for the CRUD action menu. | No |
The persist-column-state-key string defines the key where the serialised state of the columns is stored, as an object in session storage.
If you set multiple entity-management components in your application, you must use unique keys to persist the state - otherwise, the user experience will be unpredictable.
For a full list of attributes and properties, see the API documents.
Customising
By default, you get a grid and a form based directly on the back-end resource that you are connecting to; you get all the fields (columns) from that resource. Equally, you get a form based on the metadata of the event you have specified.
Customising the grid
If you want to control the appearance of the grid, use the columns attribute. This enables you to supply an array of ColDef[] properties to configure the columns that are displayed, their width and many other properties; these are the same properties that are used by the Grid Pro component.
The example array below creates six columns, specifying the width of each one.
- The
fieldis the field in the data source. - The
headerNameis the text displayed in the column heading. - Three of the fields use
cellStyleto control the alignment of the values displayed. - One field (whose column heading is "Status") also uses
cellStyleto control the colour of the values displayed.
{field: "REQUEST_VERSION", headerName: "Version", width:90},
{field: "REQUEST_STATUS", headerName: "Status", width:80, cellStyle: {'text-align': 'right', 'color': 'red'}},
{field: "SALES_PERSON", headerName: "Sales", width:100},
{field: "PRODUCT", headerName: "Product", width:100, cellStyle: {'text-align': 'center'}},
{field: "CLIENT_NAME", headerName: "Client", width:100},
{field: "NOTIONAL", headerName: "Notional", width:100, cellStyle: {'text-align': 'left'}},
As a result of these column definitions, the following grid is displayed:
Customising the buttons on the grid
By default, the grid displays Add, Edit and Delete buttons to match the settings you have made for createEvent (insert), updateEvent (edit) and deleteEvent. These are placed above the grid to the right. Edit and Delete buttons are greyed out until the user selects a row in the grid.
You can set the location of the buttons using the setting crud-menu-position.
- To position the Edit and Delete buttons in a column for every row in the grid, set
crud-menu-position = column.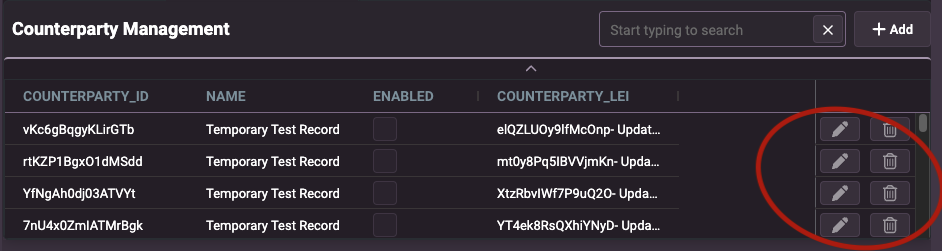
- If you don't want to display the buttons at all, set
crud-menu-position = none.
You can set the style of the buttons using the crud-menu-style setting. This hides the buttons and displays a small button with three vertical dots. When the user clicks on the three dots, the available buttons are then displayed for the user to select.
- With
crud-menu-style = actions-horizontal, when the user clicks on the dots, the buttons are displayed horizontally (side-by-side). - With
crud-menu-style = actions-vertical, when the user clicks on the dots, the buttons are displayed vertically.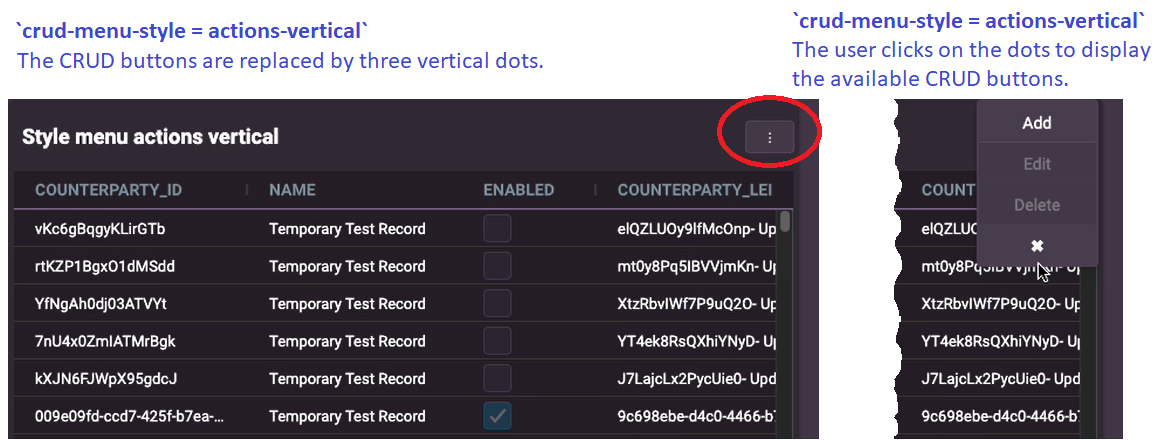
Adding default values to the form
To provide default values for when the form is displayed, use the defaultEntityValues attribute and supply an object that contains the default values. For example:
<entity-management
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_COUNTERPARTYS"
:defaultEntityValues="${(x) => defaultData}"
createEvent="EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_INSERT"
></entity-management>
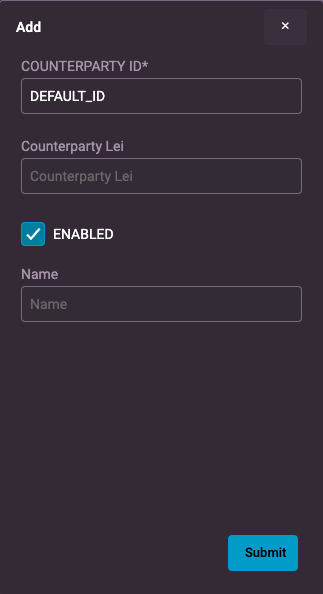
Here is a very simple object that provides one default value:
const defaultData = {
COUNTERPARTY_ID: 'DEFAULT_ID',
ENABLED: true,
};
And here we can see that default value in the form:
Customising the form
If you want to control the content of a form - for example, you might want to use different forms for inserting a new record and for modifying an existing record - use either the createFormUiSchema attribute or the updateFormUiSchema attribute. These enable you to provide a schema that configures the form.
There is a lot of useful information about defining and customising forms in our section on Forms, along with working examples.
You can also find detailed information about using these attributes in the API documentation.
Customising colours, fonts and more
Your designtokens.js contains the details of the default fonts, colours, borders and padding, all of which control the appearance of your user interface.
The easiest way to change this file is to run the Design System Configurator, where you can change settings and instantly see how they look on screen. Once you have made changes that suit you, you can click on the Save button to save the settings directly to the designtokens.js file in your repo.
To run the Design System Configurator, make sure your project is running; from the client directory of your app, run:
npm run dsconfig
Slots
A slot is essentially a placeholder where you can define content and actions for a component - such as menu buttons. The slots are generated dynamically, based on the value of the crud-menu-position attribute.
Static slots
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
header | The content to be displayed in the header section. If crud-menu-position is set to top, this slot content will overwrite the crud-top content. |
footer | The content to be displayed in the footer section. If crud-menu-position is set to bottom, this slot content will overwrite the crud-bottom content. |
Dynamic slots
You can set the crud-menu-position attribute to one of the following values: column, top, bottom, action.
Based on this value, the following slots will be available:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
crud-{position}-before | The content to be displayed before the specified position |
crud-{position} | The main content for the specified position |
crud-{position}-after | The content to be displayed after the specified position |
Default behaviour
- The default value for
crud-menu-positioniscolumn. - If
crud-menu-positionis set tobottomand thefooterslot is also set inentity-management, thefooterslot content will overwrite thecrud-bottomcontent. - Similarly, if
crud-menu-positionis set totopand theheaderslot is also set inentity-management, theheaderslot content will overwrite thecrud-topcontent.
Examples
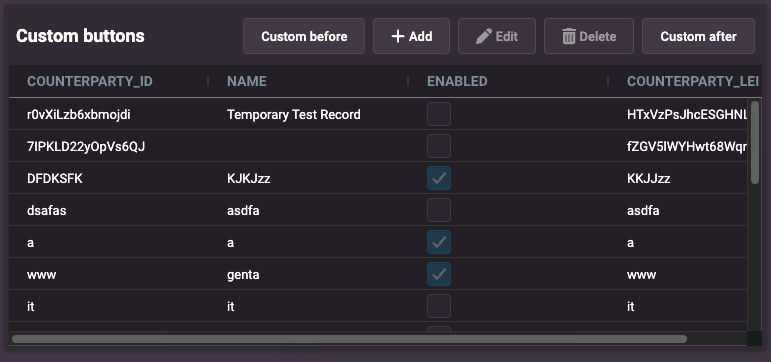
Example 1: crud-menu-position set to top
<entity-management
design-system-prefix="rapid"
crud-menu-position="top"
resourceName="ALL_COUNTERPARTYS"
title="Custom buttons"
updateEvent="EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_MODIFY"
deleteEvent="EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_DELETE"
createEvent="EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_INSERT"
>
<rapid-button slot="crud-top-before">Custom before</rapid-button>
<rapid-button slot="crud-top-after">Custom after</rapid-button>
</entity-management>
preview:
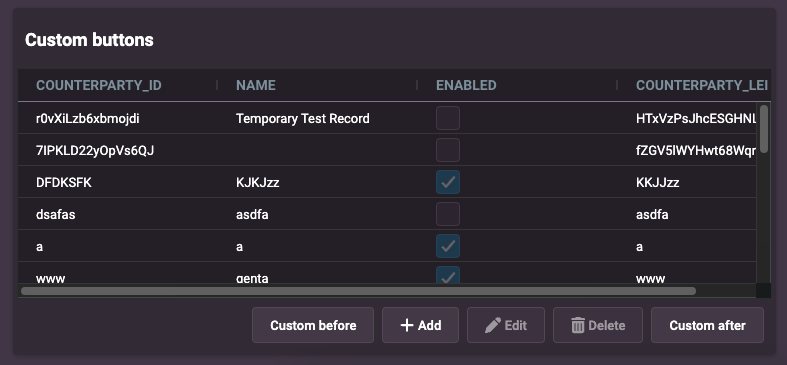
Example 2: crud-menu-position set to bottom
<entity-management
design-system-prefix="rapid"
crud-menu-position="bottom"
resourceName="ALL_COUNTERPARTYS"
title="Custom buttons"
updateEvent="EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_MODIFY"
deleteEvent="EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_DELETE"
createEvent="EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_INSERT"
>
<rapid-button slot="crud-bottom-before">Custom before</rapid-button>
<rapid-button slot="crud-bottom-after">Custom after</rapid-button>
</entity-management>
preview:
- If you create multiple slots of content or actions, the slots will be placed side by side.
- Ensure that the
crud-menu-positionis set appropriately to avoid conflicts with theheaderandfooterslots. - The dynamic slots (
crud-{position}-before,crud-{position},crud-{position}-after) are generated inside theheaderandfooterslots. Therefore, if theheaderorfooterslots contain content, they will overwrite the dynamic slots.
User Management
The User Management business component has been built using the Entity Management micro front-end.
It is designed to enable you to configure user access to the system with the minimum of effort.
Profile Management
The Profile Management micro front-end provides a way of managing the profiles on the front end. This has been built using the Entity Management micro front-end.
It is designed to enable you to configure the user profiles with the minimum of effort. These user profiles control access to specific functions and information in your application.