Timestamps - GenesisFlake
When you generate a database on the Genesis low-code platform, every table in the database is given a timestamp field. This contains a timestamp value that is generated automatically by GenesisFlake every time a change is made to the database. The TIMESTAMP field in GenesisFlake represents the creation time of a record, not the last modified time.
To create these values, GenesisFlake generates IDs in a similar manner to Twitter’s snowflake. It is able to generate these IDs without having to perform database-level synchronisation - which ensures high performance.
An ID includes:
- a node number (which represents the node id within a Genesis cluster)
- a sequence number (used to differentiate IDs generated within the same millisecond)
Format
The GenesisFlake timestamp is made up of:
- epoch time in milliseconds
- node id
- sequence id
The timestamp itself is stored in the most significant bits of a LONG variable, leaving the least significant bits to node id and sequence number.
A raw ID value looks like this, for example: 6626101958220449352.
You can extract the timestamp component using bitwise right-shift operations. For example:
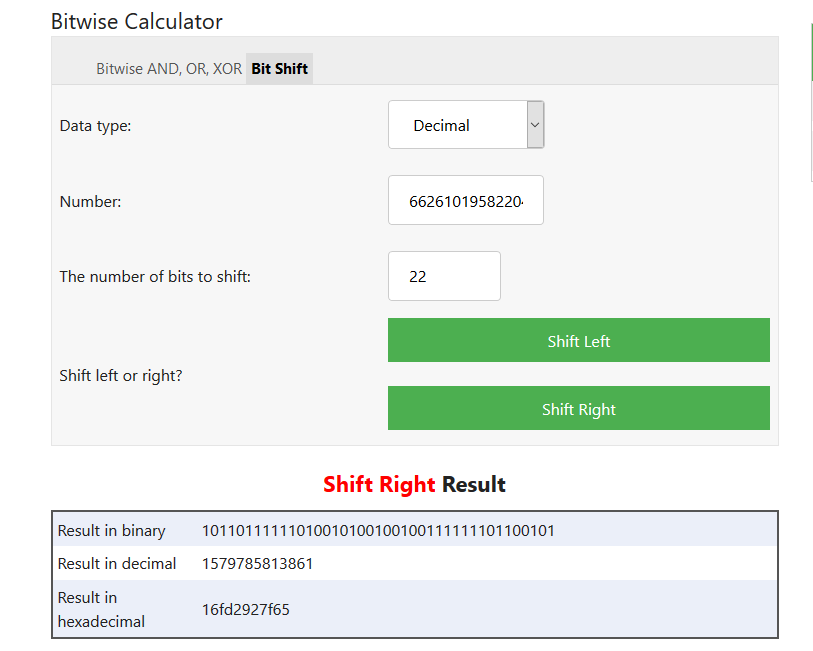
The result in decimal corresponds to 1579785813861, which can be checked in https://www.epochconverter.com/