Foundation Forms - filters
A filter is a display that connects to a server resource, such as a Data Server. It enables the user to set one or more fields from the resource to filter information. For example, the user could select trades with a specific broker or trades within a specified value range.
To create a filter, your main tasks are:
-
Specify the server resource where the underlying information is coming from.
-
Configure the layout using a UI schema (Optional).
In order to display the filtered information, you need to specify another component and synchronise it with the information in the filter.
Examples
Add a filter
Below is an example of a foundation-filters using the resourceName attribute. This attribute must be a resource from the server such as dataserver or request server; in this case, we are using a data server called ALL_TRADES.
<foundation-filters design-system-prefix="rapid" resourceName="ALL_TRADES"></foundation-filters>
Generated Criteria:
Configure form using UI schema
You can provide a UISchema to the filter in order to customise which fields should be displayed in the filter forms. In the example below, we set only the fields QUANTITY and SIDE.
- Genesis
- React
- Angular
Declaration:
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_TRADES"
:uischema=${(x) => x.uiSchema}
></foundation-filters>
Usage:
const uiSchemaExample = {
type: "VerticalLayout",
elements: [
{
type: "Control",
scope: "#/properties/QUANTITY",
label: "Quantity",
},
{
type: "Control",
scope: "#/properties/SIDE",
label: "Side",
},
],
};
@customElement({
name: 'filters-example',
template: html`
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_TRADES"
:uischema=${x => uiSchema}
></foundation-filters>
`,
})
export class FiltersExample extends GenesisElement {
uiSchema: UiSchema = uiSchemaExample;
}
Declaration:
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_TRADES"
uischema={uiSchema}
></foundation-filters>
Usage:
const uiSchemaExample = {
type: "VerticalLayout",
elements: [
{
type: "Control",
scope: "#/properties/QUANTITY",
label: "Quantity",
},
{
type: "Control",
scope: "#/properties/SIDE",
label: "Side",
},
],
};
export default function FiltersExample({}) {
const uiSchema: UiSchema = uiSchemaExample;
return (
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_TRADES"
uischema={uiSchema}
></foundation-filters>
);
}
Declaration
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_TRADES"
[uischema]="uiSchema"
></foundation-filters>
Usage
import { Component, CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
const uiSchemaExample = {
type: "VerticalLayout",
elements: [
{
type: "Control",
scope: "#/properties/QUANTITY",
label: "Quantity",
},
{
type: "Control",
scope: "#/properties/SIDE",
label: "Side",
},
],
};
@Component({
selector: 'my-root',
template: `
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_TRADES"
[uischema]="uiSchema"
></foundation-filters>
`,
standalone: true,
schemas: [CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA],
imports: [FormsModule],
})
export class AppComponent {
uiSchema = uiSchemaExample
}
Configure form using JSON schema (optional)
You can configure the information that is retrieved from the server by providing a JSON schema on the client, instead of providing a resourceName. The resourceName gives you all the fields that have been specified in the event on the server. But, with a hard-coded schema, you can change the fields and their order. However, note that if a field changes name or type on the server, you will have to change this in the schema, or it will not work.
Here is an example of configuration that is returned by the server:
- Genesis
- React
- Angular
Declaration:
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_INSTRUMENTS"
:jsonSchema=${(x) => x.jsonSchema}
></foundation-filters>
Usage:
export const jsonSchemaExample = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
INSTRUMENT_ID: {
type: 'string',
minLength: 3,
description: 'kotlin.String',
},
QUANTITY: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.Double',
},
},
};
@customElement({
name: 'filters-example',
template: html`
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_INSTRUMENTS"
:jsonSchema=${(x) => jsonSchema}
></foundation-filters>
`,
})
export class FiltersExample extends GenesisElement {
jsonSchema: JSONSchema7 = jsonSchemaExample;
}
Declaration:
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_INSTRUMENTS"
jsonSchema={jsonSchema}
></foundation-filters>
Usage:
export const jsonSchemaExample = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
INSTRUMENT_ID: {
type: 'string',
minLength: 3,
description: 'kotlin.String',
},
QUANTITY: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.Double',
},
},
};
export default function FiltersExample({}) {
const jsonSchema: JSONSchema7 = jsonSchemaExample;
return (
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_INSTRUMENTS"
jsonSchema={jsonSchema}
></foundation-filters>
);
}
Declaration
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_INSTRUMENTS"
[jsonSchema]="jsonSchema"
></foundation-filters>
Usage
import { Component, CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
export const jsonSchemaExample = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
INSTRUMENT_ID: {
type: 'string',
minLength: 3,
description: 'kotlin.String',
},
QUANTITY: {
type: 'number',
description: 'kotlin.Double',
},
},
};
@Component({
selector: 'my-root',
template: `
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_INSTRUMENTS"
[jsonSchema]="jsonSchema"
></foundation-filters>
`,
standalone: true,
schemas: [CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA],
imports: [FormsModule],
})
export class AppComponent {
jsonSchema = jsonSchemaExample;
}
Synchronising values with datasource criteria
If you want to synchronise your filter with another display (such as a grid-pro) for Genesis Component syntax, follow these steps:
- Create an
@observablevariable to store the criteria used in thefoundation-filter:
import {... , observable} from '@genesislcap/web-core';
...
export class TEMPLATE extends GenesisElement {
...
@observable allTradesFilters: string
...
}
- In your template, use the
syncfunction to save the criteria value from the foundation filter into the variableallTradesFilters:
import {sync} from '@genesislcap/foundation-utils';
...
...
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_USERS"
:value=${sync((x) => x.allTradesfilters)}>
</foundation-filters>
...
...
From this point, the criteria used in the foundation-filter are stored in the allTradesFilters variable. You can use this variable with the <grid-pro-genesis-datasource> to match the criteria used in the foundation filter.
- Assign the
allTradesFiltersto thecriteriaattribute of the<grid-pro-genesis-datasource>.:
<zero-grid-pro>
<grid-pro-genesis-datasource
resource-name="ALL_TRADES"
criteria=${(x) => x.allTradesFilters}
></grid-pro-genesis-datasource>
</zero-grid-pro>
The outcome is that the foundation-filter displays a form showing all the available fields in the resource. This enables the user to select specific criteria for each field. Beneath this, the zero-grid-pro displays the data filtered by the input criteria.
Filter persistence
Foundation Filters can be saved to the server and retrieved from the UI using the attribute "show-filter-persistence-controls"
import {sync} from '@genesislcap/foundation-utils';
...
...
<foundation-filters
design-system-prefix="rapid"
resourceName="ALL_USERS"
:value=${sync((x) => x.allTradesfilters)}>
show-filter-persistence-controls
</foundation-filters>
...
...
This will show additional controls within the filter form that allow the user to create and delete filters. These filters are persisted on the back end using the Key Value storage feature Key Value storage:
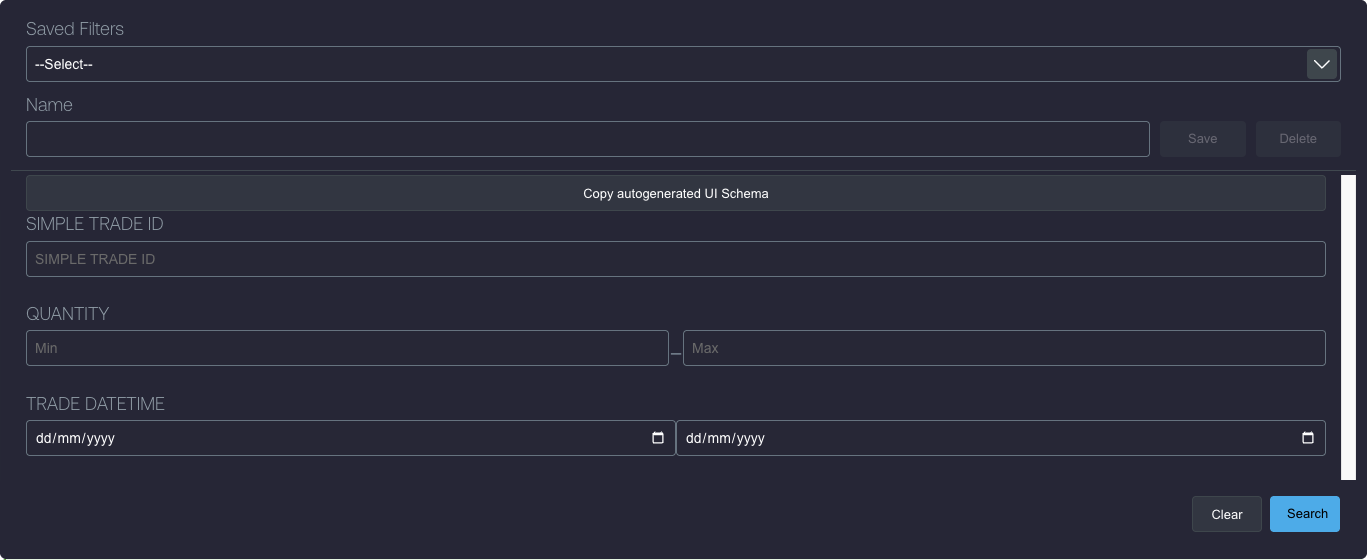
It is crucial to manipulate the style of the foundation-filter in order to see the zero-grid-pro beneath it.
After you have looked at the basics here, you can find more details in our API Docs