Foundation Forms - validation
You can apply simple or more complex validation logic to foundation forms in a number of ways.
Examples
Required fields - front end
To make a field required, include the field name in the json schema required property.
This example extends our previous example schema with the required fields.
const requiredFieldsJsonSchema: JSONSchema7 = {
...singleColumnJsonSchema,
required: ["USER_NAME", "PASSWORD", "PASSWORD_CONFIRMATION"],
}
If you focus and blur, or try submitting the form with the fields not filled, you will see the relevant error messages.
For all required fields, the form label will be appended with a * to indicate to the user that it is required.
Required fields - auto-generated schema from the back end
If you are using the reseourceName property on your form, this uses the generated json schema from the corresponding type.
Using the EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_INSERT event endpoint, your template looks like this (e.g. just passing the event name).
<foundation-form resourceName="EVENT_COUNTERPARTY_INSERT">
</foundation-form>
This is based on the model defined in your tables and event handler files. The notNull() fields will be required in the form.
eventHandler<Counterparty>("COUNTERPARTY_INSERT", transactional = true) {
onCommit { event ->
val details = event.details
entityDb.insert(details)
ack()
}
}
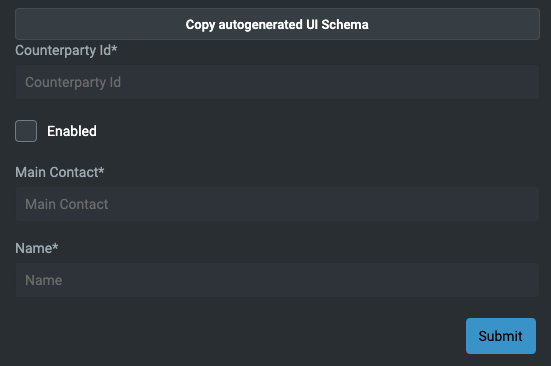
You will see an autogenerated form. Remember, you can override the appearance using the uiSchema attribute on the foundation-form element.
...
table(name = "COUNTERPARTY", id = 11_001) {
field("COUNTERPARTY_ID", INT).notNull()
field("ENABLED", BOOLEAN).default(false).notNull()
field("MAIN_CONTACT", STRING).notNull()
field("NAME", STRING).notNull()
primaryKey("COUNTERPARTY_ID")
}
...
Min Length, Max Length
A common requirement in a form field is to have a minimum or maximum number of characters, or a min or max value. This is easily achieved using the json schema.
Specify the minLength or maxLength property for the individual schema element; here is an example:
export const validationMinMaxLengthJsonSchema: JSONSchema7 = {
properties: {
minLengthInput: {
type: 'string',
minLength: 3,
},
maxLengthInput: {
type: 'string',
maxLength: 10,
}
},
required: [ 'minLengthInput', 'maxLengthInput']
}
The result is that your form will validate the number of characters.
Min Value, Max Value
Another common requirement in a form field is to have a minimum or maximum value. Again, this is easily achieved using the json schema.
Specify the minimum or maximum property for the individual schema element; here is an example:
export const validationMinMaxValueJsonSchema: JSONSchema7 = {
properties: {
minValueInput: {
type: "number",
description: "kotlin.Double",
minimum: 18,
},
maxValueInput: {
type: "number",
description: "kotlin.Double",
maximum: 65,
},
},
required: ["minValueInput", "maxValueInput"],
};
The form will show any errors if you try to submit or blur an element.
Error messages
When validation fails, Foundation Forms shows a human‑readable error message under the affected field. The exact text depends on the rule that failed and can come from the JSON schema, the UI schema, or a default message.
Typical default messages include:
- Required fields: shown when a property listed in
requiredis empty, for example:This field is required. - Length limits: for
minLength/maxLength, for example:Must be at least N charactersorMust be at most N characters. - Value limits: for
minimum/maximum, for example:Must be greater than or equal to NorMust be less than or equal to N. - Pattern validation: for
pattern, for example:Value does not match the required format. - AnyOf / OneOf: when using composition keywords like
anyOf, Foundation Forms computes a user‑friendly message for the control using thegetAnyOfErrorMessagehelper.
You can override the default text using JSON schema or UI schema configuration:
- JSON schema: use the standard
errorMessagekeyword from JSON schema. This is applied whenever that rule fails for the field. - UI schema: you can provide a custom error message for a specific control via the UI schema options. When both are present, the UI schema message takes precedence over the JSON schema
errorMessageand the generic fallback.
This lets you start with sensible defaults and then refine individual error messages to match your product wording and UX guidelines.
JSON schema examples
Below are simple JSON schema examples for each error message type:
Required field message
const schemaWithRequiredError: JSONSchema7 = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
username: {
type: 'string',
},
},
required: ['username'],
errorMessage: {
required: {
username: 'Username is required',
},
},
};
Min / max length messages
const schemaWithLengthErrors: JSONSchema7 = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
password: {
type: 'string',
minLength: 8,
maxLength: 32,
},
},
errorMessage: {
properties: {
password: {
minLength: 'Password must be at least 8 characters long',
maxLength: 'Password must be at most 32 characters long',
},
},
},
};
Min / max value messages
const schemaWithValueErrors: JSONSchema7 = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
age: {
type: 'number',
minimum: 18,
maximum: 65,
},
},
errorMessage: {
properties: {
age: {
minimum: 'Age must be 18 or older',
maximum: 'Age must be 65 or younger',
},
},
},
};
Pattern message
const schemaWithPatternError: JSONSchema7 = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
email: {
type: 'string',
pattern: '[a-z0-9._%+-]+@[a-z0-9.-]+\\.[a-z]{2,4}$',
},
},
errorMessage: {
properties: {
email: 'Please enter a valid email address',
},
},
};
AnyOf / OneOf message
const schemaWithAnyOfError: JSONSchema7 = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
contact: {
anyOf: [
{
type: 'string',
format: 'email',
},
{
type: 'string',
pattern: '^\\+?[0-9]{7,15}$',
},
],
errorMessage: {
anyOf: 'Enter a valid email address or phone number',
},
},
},
};
Pattern validation
You can validate the input of your field using regex to ensure the user enters a certain pattern of characters.
A common use case for this is validating phone number or email input data.
export const validationPatternJsonSchema: JSONSchema7 = {
type: 'object',
properties: {
phoneNumber: {
type: 'string',
pattern: '^[\\+]?[(]?[0-9]{3}[)]?[-\\s\\.]?[0-9]{3}[-\\s\\.]?[0-9]{4,6}$',
description: 'kotlin.String',
},
email: {
type: 'string',
pattern: '[a-z0-9._%+-]+@[a-z0-9.-]+\.[a-z]{2,4}$',
description: 'kotlin.String',
}
},
required: ['phoneNumber']
}
export const validationPatternUiSchema: UiSchema = {
type: 'VerticalLayout',
elements: [
{
type: 'Control',
scope: '#/properties/phoneNumber'
},
{
type: 'Control',
scope: '#/properties/email'
}
],
}
After you have looked at the basics here, you can find more details in our API Docs
Full source code at Validation