Server configuration - database technology
The Genesis low-code platform supports the following database technology:
- H2
- FoundationDB
- Postgres (PostgreSQL)
- MSSQL
- Oracle
Because we abstract from the underlying technology, you can easily toggle between any of these four.
There are also tools that enable you to stream real-time data reliably to and from any classic Oracle/SQL database.
By default, H2 is installed on the platform. This is ideal for simple local development, but once you are ready for serious development, and when you need a production envronment, you must set up one of the other databases that we support.
To change the database technology, follow the steps below.
If you do not set the database correctly, this will cause fundamental errors. You will not be able to run genesisInstall or remap correctly.
Changing the database technology
1. Edit the system configuration file
Edit the system definition file: ~/run/site-specific/cfg/genesis-system-definition.kts. Before you start, make sure you know the JDBC connection string for the database, which specifies the host, the username and password.
You need to make two changes.
First, go to the line item for DbLayer and change the value from H2 to SQL (for Postgres, Oracle or MSSQL).
systemDefinition {
global {
item(name = "MqLayer", value = "ZeroMQ")
item(name = "DbLayer", value = "SQL")
item(name = "DictionarySource", value = "DB")
Then, insert a line in the hosts block to identify the JDBC connection string for the database. This points the system to the local Postgres, Oracle or MSSQL server. For example:
item(name = "DbHost", value = "jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres?user=postgres&password=Password5432")
Here is the example in place:
systems {
system(name = "DEV") {
hosts {
host(name = "genesis-serv")
}
item(name = "DbHost", value = "jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres?user=postgres&password=Password5432")
item(name = "DbNamespace", value = "genesis")
item(name = "ClusterPort", value = "6000")
item(name = "Location", value = "LO")
item(name = "LogFramework", value = "LOG4J2")
item(name = "LogFrameworkConfig", value = "log4j2-default.xml")
}
}
If you are using Postgres and you want to use a reserved keyword as a column name, then you need to add the setting below to your system definition file. This enables Quoted Identifiers to be used:
item(name = "DbQuotedIdentifiers", value = "true")
2. Activate the new configuration
Run genesisInstall.
3. Create new default table structures
Run remap --commit. This populates the database server with table structures.
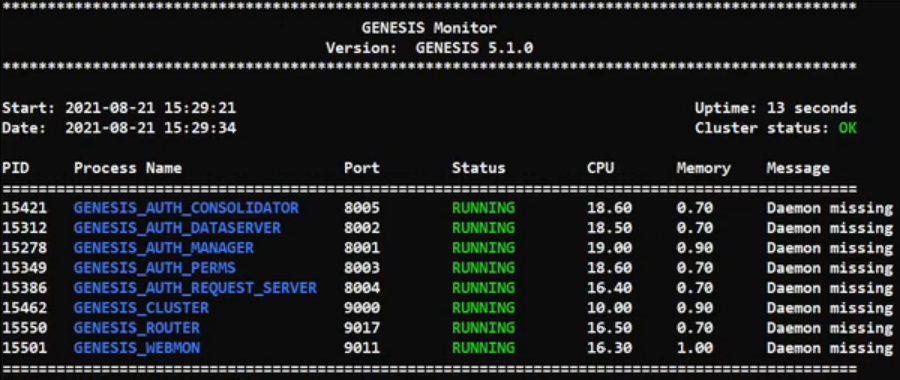
4. Start the server and check
When those three steps have been completed, run startServer to start all the processes.
On completion, run mon, and you can see the processes running. You have successfully completed the change.